
#LEG COMPARTMENT MUSCLES SKIN#
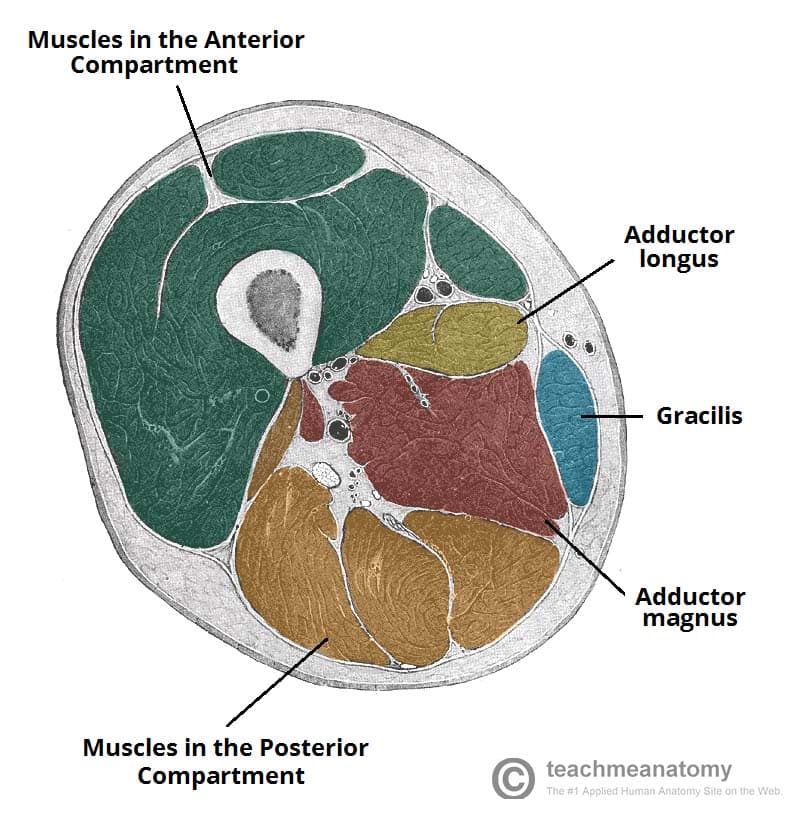
Careful use of elastic retention sutures (elastic vessel loop woven through skin staples) can help counteract skin contraction, and be tightened progressively as swelling resolves. Anterior compartment (blue): Tibialis anterior, extensor muscles of the foot, and fibularis (peroneus) tertius muscles. This is only permissible if it can be achieved without any skin tension it is inadvisable in smokers, who have impaired capacity for soft-tissue healing.įasciotomy wound edges tend to retract and become difficult to close. It is tempting to the surgeon to try early secondary skin suture, rather than skin-graft coverage, once the swelling has subsided. The simplest and safest technique is to cover the healthy soft-tissue defect with a split skin graft: at a later date, when the limb contours have returned to normal, the grafted area can be excised and secondary skin closure performed without tension. Once any skeletal injury is under control, the fasciotomy wound(s) healthy and the swelling of the soft tissues has sufficiently regressed, consideration must be given to achieving skin coverage. Reperfusion injury is another cause of compartment syndrome. After blood flow is restored, capillaries leak and ischemic muscle swells. An arterial injury may cause compartmental tissue ischemia.Muscle tolerates short periods of hypoxia, but after a few hours, progressive necrosis begins.(MPP has also been called "Delta P", to indicate the difference between diastolic blood pressure and intramuscular pressure.) This difference in pressure reflects tissue perfusion far more reliably than the absolute intramuscular pressure. The critical measurement is muscle perfusion pressure (MPP), the difference between diastolic blood pressure (dBP) and measured intramuscular tissue pressure.if diastolic arterial pressure is not more than 30 mm Hg above tissue pressure, compartmental capillary blood flow is significantly obstructed and severe hypoxia occurs in muscle and nerve tissue.When tissue pressure approaches the diastolic pressure, capillary blood flow ceases. The arterial supply is through the anterior tibial artery. These muscles are collectively innervated by the deep fibular nerve (L4-S1). Chronic exertional compartment syndrome is an exercise-induced muscle and nerve condition that causes pain, swelling and sometimes disability in the affected muscles of the legs or arms. The capillary filling pressure is essentially diastolic arterial pressure. The muscles in the anterior compartment of the leg are a group of four muscles that act to dorsiflex and invert the foot. This critical level is the tissue pressure which collapses the capillary bed and prevents low-pressure blood flow through the capillaries and into the venous drainage. Together with the interosseous membrane, they divide the muscles of the leg into four compartments, two on the front of the leg, and. Compartment syndrome most often occurs in the anterior (front) compartment of the lower leg (calf). Compartment syndrome occurs when the pressure within a closed osteo-fascial muscle compartment rises above a critical level.Action: Extension of the great toe and dorsiflexion of the foot.The tendon crosses anterior to the ankle joint and attaches to the base of the distal phalanx of the great toe. Attachments: Originates from the medial surface of the fibular shaft.Its tendon emerges from between the two muscles to insert onto the big toe. The extensor hallucis longus is positioned deep to tibialis anterior and extensor digitorum longus. Actions: Extension of the lateral four toes, and dorsiflexion of the foot.The tendon splits into four and each tendon inserts onto a toe.The fibres converge into a tendon, which travels onto the dorsal surface of the foot.Originates from the lateral condyle of the tibia and the medial surface of the fibula.Some of the largest and most powerful muscles in the body are the gluteal muscles or gluteal group.
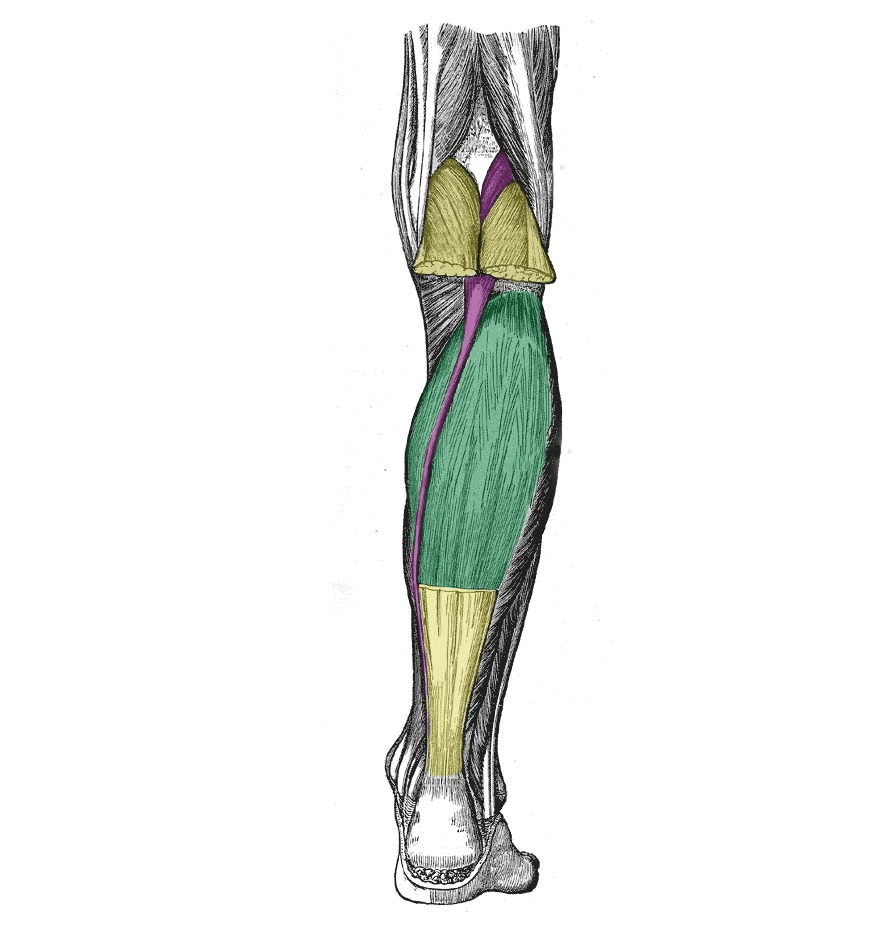
Its four tendons can be palpated on the dorsal surface of the foot. The psoas major and iliacus make up the iliopsoas group. The leg is separated into anterior, lateral, superficial posterior and deep posterior compartments by intermuscular septa and surrounded by the deep. Muscles within this compartment primarily produce ankle dorsiflexion and toe extension.
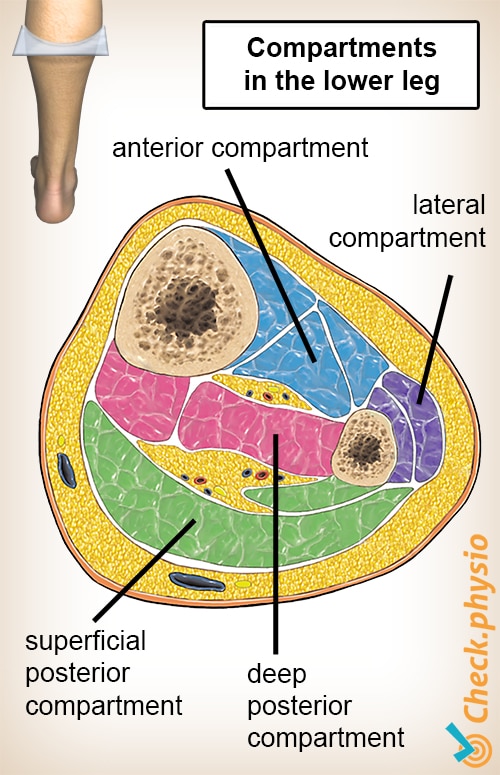
The extensor digitorum longus lies laterally and deep to the tibialis anterior. The anterior compartment of the leg is one of the four compartments in the leg between the knee and foot.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
